Axiado is launching a free ransomware detection and analysis service/platform for both security professionals and everyday users. This service is called Ransomware Threat Hunting Service (RTHS) or simply a sandbox. This service is driven by Axiado’s AI/ML-based security co-processor and incorporates a multitude of open-source software tools designed for ransomware analysis. In addition, integrated threat hunting software suite used by this service will be open sourced so that others can also host the software suite in their preferred environment/eco-system.
Given the immense challenges of detecting and countering the myriad of ransomware variants and their unique attack patterns, leveraging crowdsourced machine learning datasets is an effective strategy to address cyberworld’s dire need to stop ransomware attacks. Dataset sharing enables the security community and users at large to more rapidly identify and thwart ransomware threats.
We invite IT and security professionals to submit the suspicious ransomware executables and scripts (e.g. python) to the sandbox to learn the ransomware’s behavior. In addition, you can use the analysis report and Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) to stop the ransomware attacks. Your contribution helps our fellow professionals in other organizations to stop the ransomware attacks on their organizations too. Your contribution is analogous to how (Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency) CISA’s ransomware analysis report helps the industry as a whole to detect and stop ransomware. Axiado’s sandbox performs live analysis of the ransomware which is a crucial and a faster way to detect and respond to ransomware attacks. Let’s work together to defeat the ransomware attacks!
Architecture and user interface
Users and security analysts can benefit from this sandbox in a couple of different ways. Those are.
- Use Axiado’s dataset to study the behavior of known ransomware families. Axiado already collected thousands of ransomware machine learning datasets from the open source and more datasets will be collected on an ongoing basis.
- Upload ransomwares or related data such as security logs. If it’s a ransomware, then RTHS will execute it and shows a detailed breakdown of actions taken by the ransomware ranging from encryption of files, privilege escalation to encrypted data exfiltration over a covert backdoor connection to the attacker’s site.
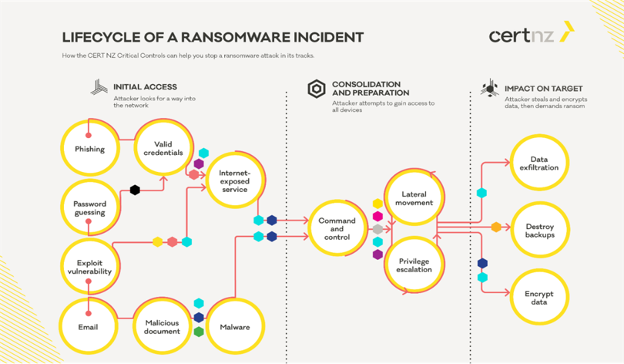
During the lifecycle of a ransomware, initial access, to all the way to successful exfiltration of the files, ransomware uses different Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs) https://attack.mitre.org/matrices/enterprise/ to progress the attack. Below diagram from CISA’s LockBit ransomware advisory https://www.cisa.gov/news-events/cybersecurity-advisories/aa23-165a shows some of the commonly used TTPs by a ransomware.
Ransomware Threat Hunting Service (RTHS) uses a variety of techniques and strategies to detect and prevent malicious activity, such as:
- Behavioral analysis: Gathers VM’s behavior for suspicious activity, such as privilege escalation to kill antivirus software running in the VM.
- Malware signatures: uses a database of known malware signatures to identify malicious applications.
- Reputation analysis: Uses reputation analysis to identify malicious applications based on their behavior and reputation. Such as launching Metasploit to exploit vulnerabilities.
RTHS uses the below technologies and methods.
- Hypervisor introspection: Hypervisor introspection is used to inspect the state of running VMs without the need to install any agents on the VMs. This allows RTHS to detect malicious applications that evade detection from traditional security solutions.
- Machine learning: Uses machine learning to identify patterns in VM behavior that are associated with malicious activity. This allows RTHS to detect new and emerging threats that traditional security solutions may not be able to detect.
- Threat intelligence: uses threat intelligence from reputed OSINT (Open Source Intelligence) companies to identify known malicious applications and signatures. This allows faster and accurate threat detection.
Ransomware detection and analysis can be done either by hosting an agent in the host (OS, VM or in a container) or it could be without running an agent (aka agentless). RTHS’s initial implementation is using the agentless model. It is using the well reputed agentless malware detection open-source solution known as DRAKVUE. RTHS integrates with OpenAI for utilizing it’s Generative AI capabilities in addition to using Axiado TCU’s (security co-processor) native AI/ML processor.
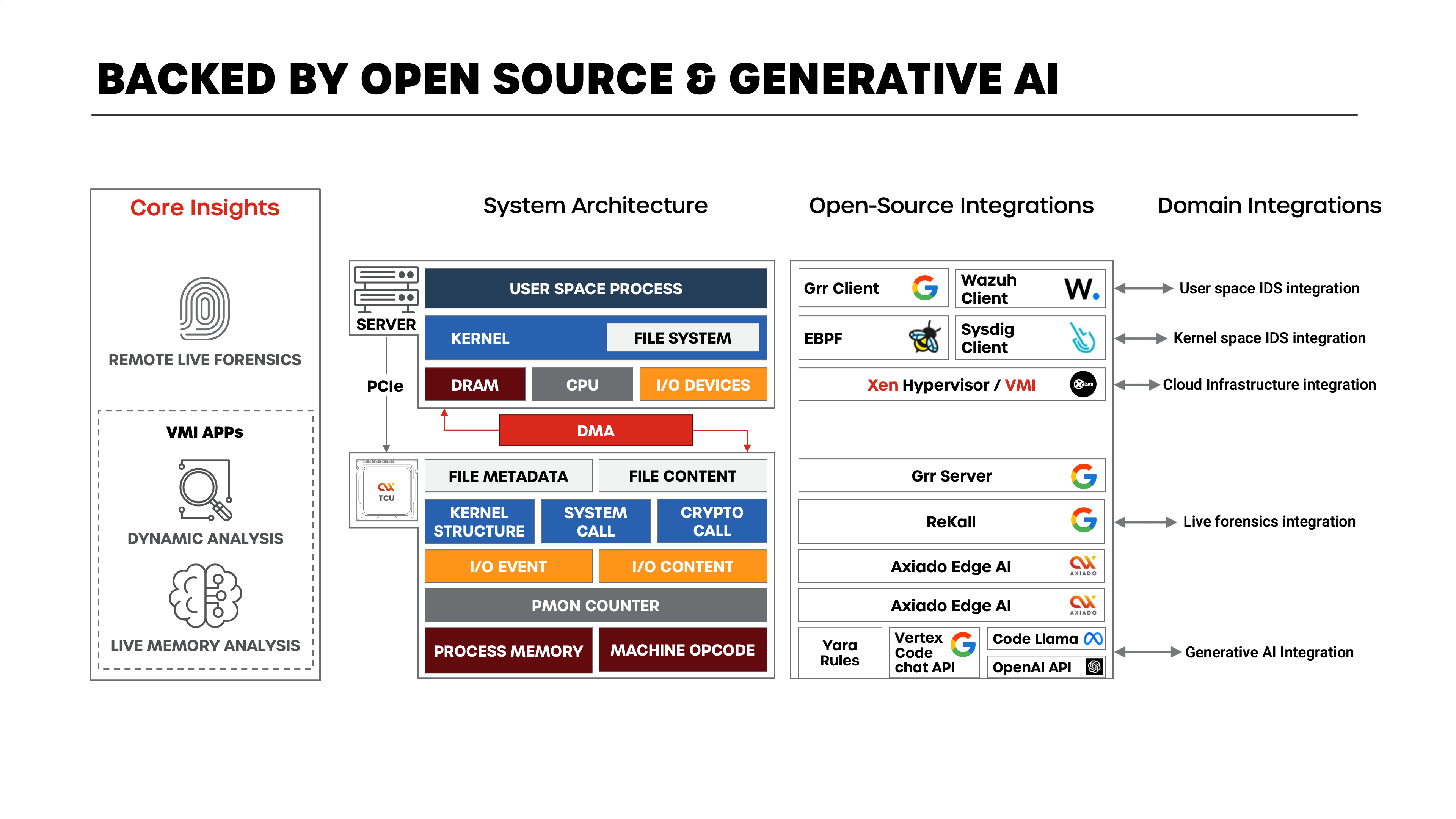
RTHS’s high level architecture vision is as below.